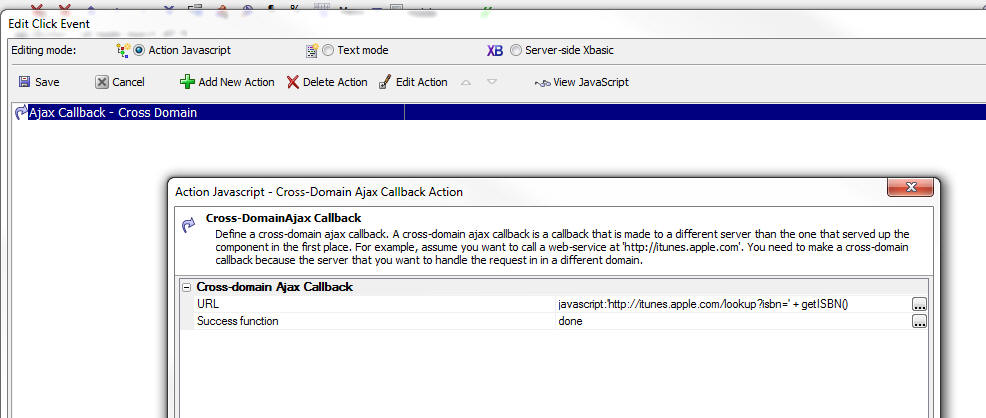
Ajax Callback - Cross Domain
Description
Define a user-defined cross-domain ajax callback. A cross-domain Ajax callback is a callback to a web service in a domain that is different from the domain from which this component was originally loaded.
Discussion
Because of security issues, browsers typically enforce a policy that requires that the page that responds to an Ajax callback must be loaded from the same domain that the original page was loaded. This does not represent a problem for typical Ajax callbacks that are handled by Xbasic code on the Alpha Anywhere server.
However in cases where you want to call a web service directly from the client (without first going to the Alpha server), it does represent a problem.
Consider for example the following scenario:
Say you have a button on the UX and you want to make a call to the Apple iTunes store to retrieve information about a book.
The URL for this web service (including the query string for the particular book you are interested in) is as follows:
http://itunes.apple.com/lookup?isbn=9780316069359
The domain for this URL is obviously not the same as the domain from which the UX component was loaded in the first place.
There are two ways in which you could call this web service:
- Make a standard Ajax callback and define an Xbasic function that calls out to the Apple web service (using the Xbasic http_get_page2() function), and then return the response from the Apple web service to the UX component in the same way that any other response from an Ajax callback is return to the UX component.
- Directly call the Apple web service from the browser
Clearly, the second approach is more desirable as it avoids hitting the Alpha server at all.
However, in order to implement the second approach you need to perform a cross-domain Ajax callback.
The 'Ajax Callback - Cross Domain' action in Action Javascript allows you to perform cross-domain Ajax callbacks.
When you define this action you specify the URL of the callback page. Any parameters that you want to pass in to the web service are in the query string. When you specify the URL, you can specify an explicit value, or any Javascript expression that evaluates to the URL. This allows you to dynamically construct the URL for the callback.
You also specify the name of a Javascript function that will be called when the Ajax callback completes successfully. The function gets passed an argument that contains the data returned by the callback.
A useful technique for seeing what data in passed to the success function is to define the following success function for your action:
function mySuccessFunction(data) {
alert(JSON.stringify(data,'','\t'));
}This function will convert the data returned by the callback into a JSON string and display it.
For more information on how to create a cross-domain Ajax Callback, watch the video below:
Cross-domain Ajax Callback
A cross-domain Ajax callback is a callback that takes places to a server that is in a different domain than the domain from which the component was loaded.
In this video we show how a callback is made to the Apple iTunes store and we contrast the difference between making the callback directly to the Apple site versus making a callback to the Alpha server first and then having the Alpha server make the call to the Apple site.
Cross-domain Ajax Callback Properties
- URL
Specify the URL for the Ajax callback. The URL will typically include a query string with parameters.
- Success function
Specify the name of the Javascript function to call when the Ajax callback completes. The function takes a single argument, 'data' that contains the JSON data returned by the callback.
- Use jQuery
Specify if the callback should be made using jQuery. If you check this option, it is necessary to load the jQuery core library. If this option is not checked, then jQuery is not required.
- Callback attribute name
(Advanced) Specify the name of the attribute to use to define the Success function name. By convention, this is typically 'callback' or 'jsonp', but the web service you are calling might use a different name.
Specifying the Callback Attribute Name
The name of the JavaScript success function is sent as part of the Ajax Callback. This success function's name is passed as the value of a URL parameter. Most sites specify the URL parameter should be named 'callback'. EG:
https://www.somewebservice.com?myid=1234&callback=myOnSuccessJavascriptFunctionName
However, a web service is not required to use 'callback'. It could be anything, such as 'onsuccess' or 'foobar':
https://www.someotherwebservice.com?myid=1234&onsuccess=myOnSuccessJavascriptFunctionName https://www.yetanotherwebservice.com?myid=1234&foobar=myOnSuccessJavascriptFunctionName
If the web service doesn't use 'callback', you can define the URL parameter's name in the Callback attribute name property.
Check the documentation for the web for how the callback JavaScript Success function is specified in the URL parameters. If the service uses 'callback', you do not need to do anything. If they expect the callback function to be specified using some other URL parameter, you must set the Callback Attribute Name property.
Limitations
UX Component Only
See Also