What are citizen developers, what business units do they live in, and what software do they use? Learn why citizen development tools are helping companies can achieve business goals faster.
Properly built business apps can streamline virtually any business process. As a result, requests for mobile apps will accelerate in companies, as business managers seek to improve efficiency and cut costs.
Unfortunately, demand for new mobile apps far exceeds the resources available to produce them. Companies are turning to new strategies and technology to close the gap.
Demand for Apps is Outpacing Development
App development has traditionally lived in the wheelhouse of Information Technology Departments, driven by professional developers. These gurus have years of training in application development, software development tools, low code platforms, and process automation.
As companies recognize the value of mobility, demand for mobile applications for consumption by business users is rising dramatically. Unfortunately, the need for easy to use, reliable, and secure apps outpaces experienced developers' ability to produce them.
Business managers are frustrated that they cannot achieve fast development and deployment of business applications. This obstacle to digital transformation is a problem that companies must solve to stay competitive.
Solving the App Development Skills Gap
Marketers, managers, and field workers with domain expertise are forced to navigate IT bureaucracy to request task-focused business apps. Even when granted, digital business projects often miss the mark because of unclear communication on business requirements.
Although business users know what they want applications or programs to do, they can't create applications themself. Instead, they must rely on a requirements gathering process and an experienced developer to build the app. Marketers, managers, and field workers with domain expertise are forced to navigate IT bureaucracy to request task-focused business apps. Even when granted, digital business projects often miss the mark because of unclear communication on business requirements.
This skills gap holds many enterprises back from the potential of wide enterprise mobility efficiencies.
Over 40% of organizations report suffering from a skills gap when it comes to app development.
Companies realize that they cannot find and hire enough developers to pay to code applications they need. They're now turning to new software and a new class of mobile app developers to get the job done.
Citizen Developers Can Build Business Apps
The term "Citizen Developers" refers to business users outside of IT using development tools to solve business problems. These people may be a line of business domain experts or business analysts. Gartner explains this new type of developer:
"A Citizen developer is a user who creates new business applications for consumption by others using development and runtime environments sanctioned by corporate IT."
By allowing citizen developers to build simple apps, organizations free IT personnel to focus on complex and mission critical development projects. Ignore this growing trend at your own peril. Ignore this new app building trend at your own peril.
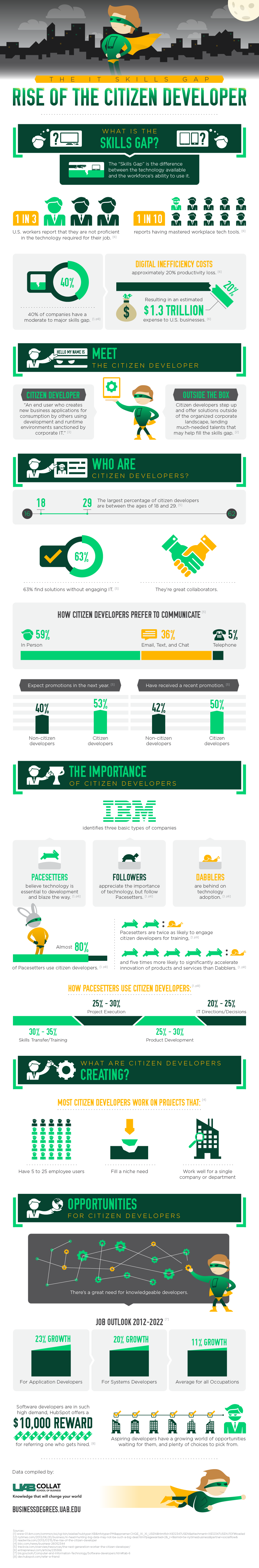
An Infographic Explaining Citizen Development
Most citizen developers are between the ages of 18 - 29. They prefer face to face communications over email or phone communications. They work on projects that serve 5-25 users and fulfill a niche need for the business.
Almost 80% of leading companies (pacesetters) are embracing new types of app builders. While less skilled than professional developers, these new app builders can craft task-based apps to power business activity.
Below is a valuable infographic from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Information Systems Program. The infographic profiles who citizen developers are in companies. It also breaks down the economic cost of the skills gap, and the ability of citizen developers to recover those costs.
This infographic finds:
- Most citizen developers are between the ages of 18 - 29.
- They prefer in-person communications over email or phone communications.
- They work on projects that serve 5-25 users and fulfill a niche need for the business.
- Almost 80% of leading companies (pacesetters) use citizen developers.
Citizen Developers Can Use Low Code Software
To succeed at mobile app development, these new app developers need simple app makers. IT cannot empower citizen developers, then learn that apps aren't secure, can't perform critical tasks or have spotty reliability.
These workers can use low-code development software or beneficial no-code application development tools to build enterprise apps. These products can create new business applications that previously could only be crafted by IT professionals. No-code software, such as drag-and-drop products, add even more flexibility.
This movement spurs the innovation of software development. IT can approve low-code software or no-code tools that are as easy to use as Microsoft Excel. Business people can solve their own problems with innovative technologies. They can even introduce new SaaS products.
How to Empower Citizen Developers to Create Mobile Apps:
How-to Guide for New App Developers:
How Companies Can Create a Culture of Citizen Development
.Understand how to identify and train new developers within your organization. Learn how to find the best low code development platform for citizen developers.
Mobile App Development Training for Citizen Developers:
How to Build a Mobile App
This step-by-step guide for beginners offers tips and resources on how to build a mobile app. Whether you're a citizen developer at a small business or a large company, you can become an app builder.
Free Software for Citizen Developers:
Free Low Code Software for Citizen Developers
Buying software for hundreds of business employees could prove very expensive. Alpha Software helps companies by providing a free development platform for these new types of mobile app builders. Create all the apps you need and only pay when you deploy the apps (for as low as $99/month).
No-Code Mobile Forms Builder for Citizen Developers
For users who simply need data collection forms, Alpha Software offers a mobile forms builder. You don't need any experience with programming to build applications using this no code app builder. It's ideal for inspections, polls, work orders, repair checklists, patient intake, and more.
The Power of The Citizen Developer. A Guest Post by Peter Darmon, the University of Alabama at Birmingham Information Systems Program, and Amy Groden, Alpha Software Corporation.
Further reading:
Citizen Developers will Outnumber Professional Developers by 4-to-1 by 2023. Gartner predicts, “active citizen developers at large enterprises will be at least four times the number of professional developers.”
Citizen Developer Governance and a Free Guide Citizen Development Center of Excellence. Low-code and no-code software are ideal for citizen developers. This technology allows groups outside of IT departments to write business applications. New IoT and machine learning possibilities add even more potential. Establish a governance framework for your organization.
How to Become a Citizen Developer. Build your own citizen development program.
A growing chorus now says that low-code platforms will do more in 2021 and beyond. These new developers will take over enterprise app development, and become a core part of IT. Read about citizen development platforms: Low-Code/No-Code: App Development In 2021 And Beyond








Comment